Analyze with AI
Get AI-powered insights from this Mad Devs tech article:
Software development is a highly volatile industry, and new project management tools, frameworks, and methodologies come and go as quickly as we create buzzwords to describe them.
Some methods, like lean development, make more sense than others, but not a single new approach, trick, or technique can dismiss the fact that "the quality of work is constrained by a project's budget, deadlines, and scope." Sometimes, we can bend the game rules a bit, but breaking them entirely is never an option.
In this article, we'll examine technical debt to discover how it emerges and why and provide solutions for resolving individual tech debt issues.

What is technical debt?
Check out our glossary entry on technical debt for a clear and succinct description of this concept. For the purposes of this article, it's enough to know that technical, or tech, debt is the price a company will pay later for choosing a simpler, faster, yet less reliable option today. Any compromise you make to release products or features faster in the present will accumulate a greater volume of work to do in the future. Moreover, technical debt—just like any other form of debt—accumulates interest unless carefully managed.
This interest makes new feature releases more expensive and less stable. Your team will waste time dealing with compatibility issues and bug fixes, and they won't be able to focus on developing new functions.
Straight to the point: Immense technical debt inflates software maintenance costs to the point where supporting the original solution is no longer an option.

Is technical debt always bad?
Tech debt isn't always bad. In fact, it's almost always unavoidable when there's a compromise between speed, cost, and quality. However, the reasons behind tech debt can lead to more severe issues later, especially if they're due to poor management decisions. Likewise, if managers ignore tech debt or make poor engineering decisions, the problem can grow into a danger to a product or company.
Why do projects fall victim to technical debt?
If tech debt sounds so bad, why do people let it become a problem? Two reasons: time and money.
Any business, big or small, needs new features. Fast! So it's no wonder borrowing time and financial resources seems like a legitimate solution.
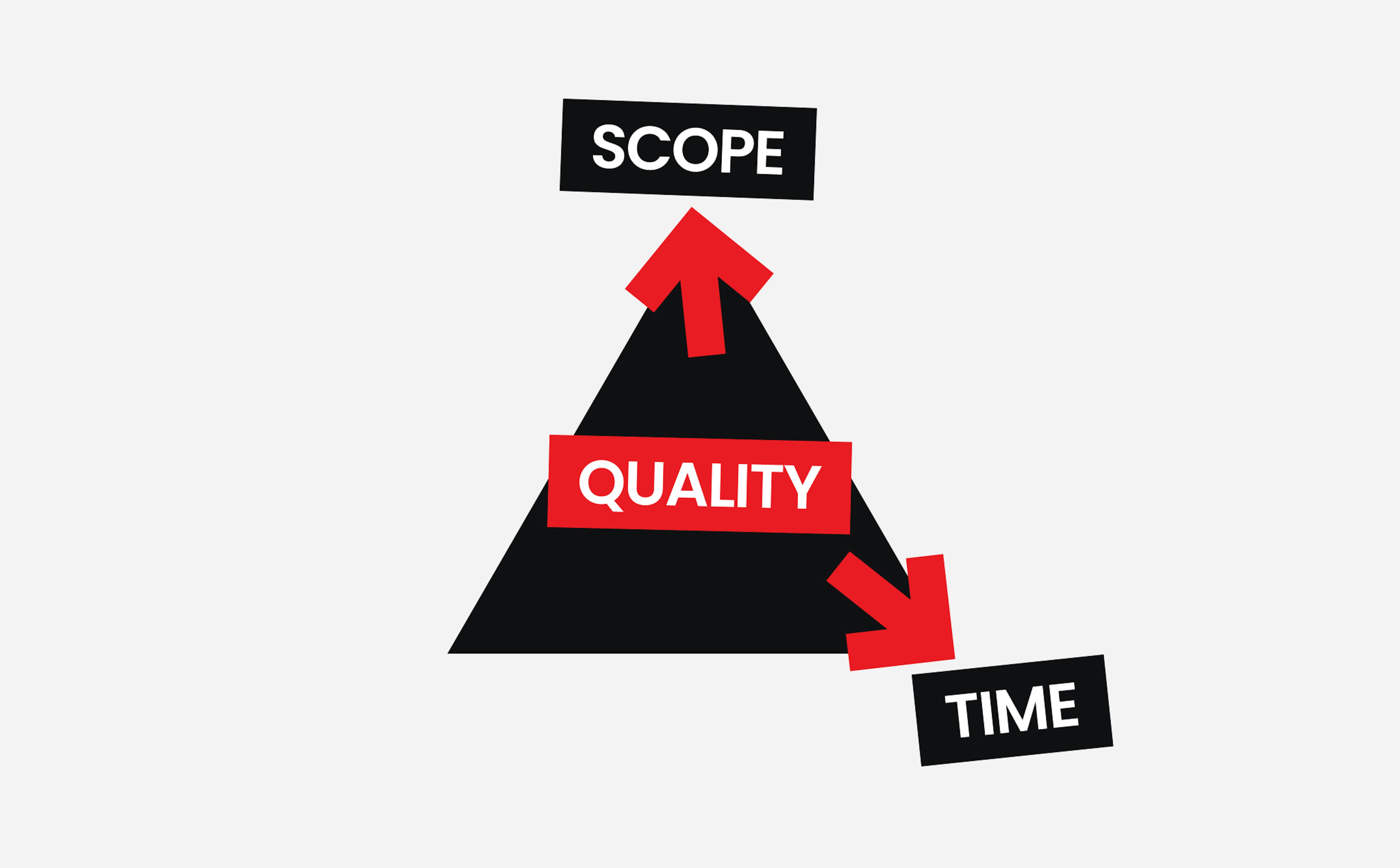
Most startups are underfunded. Apart from the competitive and volatile markets, the lack of resources is often cited as the primary reason for product failure. In other words, two of the three sides of the iron triangle are off the table before development begins.
Yet, young entrepreneurs and seasoned veterans of the investment scene take the risk. Everyone wants to be in the 1% of successful small companies that make it to the top.
Few truly care about technical debt because technical debt isn't the main factor determining whether a startup will promptly raise investment. The most important factors are time to market, competition, and a growing user base.

Then there are enterprises, the huge players who are pretty slow in adopting change. These companies have spent years and decades perfecting business processes tailored to maximize profit and ROI.
These companies are often run by people with a business-first mindset who lack a strong background in IT. Sadly, they see development as a bottomless pit of unnecessary investment.
Why waste $100K on refactoring if the product works as is?
Why invest in experienced coders when middle or junior engineers are speaking the same language?
Why waste time designing architecture when the market demands new functionality?
These and similar questions trouble the minds of decision-makers and product owners with a business background. To sum up, these realities lead to situations that lead teams to fall into debt:
- Time pressure: Developers often face the pressure to deliver the product on time. This might lead to deploying apps that are not fully featured or contain bugs. Development teams might sacrifice an app's performance to get to the market as quickly as possible.
- Market change: Even if you release a fully featured app, you might face changes in customer expectations. New market opportunities present challenges to a company.
- Outdated technology: To develop an application, you need several coding languages, developer frameworks, and libraries, which can become obsolete and lose support over time.
These overarching reasons result in specific examples of tech debt, which we will examine below.
The implications of being in debt to your own product
Immense technical debt affects the bottom line. What do you do when a website you're trying to access fails to load quickly? The odds are you'll leave to look for a different website. 53% of mobile users will flee if a website fails to load within 3 seconds. The same can be said about any product that continuously experiences downtime due to the system's painful introduction of new features.
Services that rely on impulse sales are the best example. Downtime inconveniences established routines, especially in the transportation industry, where customers continuously interact with taxi services. People are late, become annoyed at lagging applications, and taxi drivers lose their profits. Moreover, transportation is a competitive market, where competitors bombard users with promo codes and offer a service that always works. Over time, each downtime shrinks the customer base. Similarly, large projects will lose their client base over time if they continuously expose their clients to bugs and downtime.
Now that you have an understanding of tech debt and its causes let's examine some of its manifestations in projects.
What are examples of tech debt?
Here are 8 examples of tech debt and practices that lead to debt, including explanations of why they are dangerous to your projects and products and how they can be resolved.
1. Legacy code
This code is old and outdated compared with newer approaches and technologies.
Reasons it's a problem:
- It may not work well with new features
- Created by developers who may have left
- Doesn't always get updated or refactored
Solutions:
- Review the code in small batches
- Prioritize refactoring and update needs
2. Insufficient testing
Not enough tests were conducted to consider all the possible scenarios in which a product could encounter difficulties. May be done to release the product faster.
Reasons it's a problem:
- The product isn't 100% ready for all possible scenarios
- Users may lose trust due to many bugs
- Security vulnerabilities
Solutions:
- Define priorities before a project; where is testing?
- Implement automated testing tools
- Plan for testing in product development
3. Poor IT leadership
When those in decision-making positions don't understand new technologies and solutions but proceed to adopt them. This can burden a company with unnecessary and/or inefficient stack.
Reasons it's a problem:
- Developers use tools now that may be replaced later by different leadership
- The tools aren't effective at solving the product's problems and may create new issues
- Could introduce new approaches regularly that stunt progress
Solutions:
- Distribute leadership among several stakeholders, including developers
- Explain to customers if a certain product or service isn't suitable for their project
4. Inferior code quality
A product's code may include hard coding, different coding styles or standards, may not have been refactored, or contain duplicating code.
Reasons it's a problem:
- Poor code will not work in all scenarios
- It can be difficult to understand
- New team members will need more time to learn and understand this code
- It leads to more complex code that is difficult to maintain
Solutions:
- Establish code standards that all team members follow
- Schedule refactoring and code cleanup into the project
- Break up code into smaller sections to clean
5. Outdated libraries or dependencies
A product uses third-party libraries or dependencies that aren't supported or that have issues.
Reasons it's a problem:
- The product will experience incompatibility with newer libraries
- Security vulnerabilities in the product's code
- The product may crash
Solutions:
- Schedule regular reviews within the project
- Automate the process to send alerts about outdated libraries
6. Unsatisfactory documentation
There may also be no documentation, or developers may hold back information on purpose or not think it's important to share.
Reasons it's a problem:
- Team and stakeholders may lack knowledge about products and services
- No or slow transfer of knowledge to other teams and members
- Decrease in value of developer's work
Solutions:
- Holding developers accountable for proper documentation
- Introducing documentation as part of DevOps and not only using technical writers
7. Leaving bugs unresolved
This is when the developers are aware of bugs but don't fix them, and new ones appear on top of the old issues.
Reasons it's a problem:
- Product and software crashes
- Decrease in customer trust
- Security vulnerabilities
Solutions:
- Make bug tracking and resolution a priority part of the development process
- Implement bug-tracking software effectively to automate the process
8. Poorly defined user requirements
A lack of understanding of what the end user should experience will result in wasted time and other resources.
Reasons it's a problem:
- Unnecessary features added to the product
- More time is required for developers to redo the product for the client
- The release deadline needs to be extended
Solutions:
- Regular communication with stakeholders to show progress and verify their vision
- Agile practices to implement changes if and when they appear
- Provide clear explanations if something won't work
Managing tech debt
The list above provides suggestions for resolving these examples of tech debt; as you have noticed, there are some common remedies for all of them. These are essential areas to consider in your project over the long term to ensure that you effectively control and manage your tech debt as a whole:
- Tests
- Documentation
- Software architecture
- Infrastructure planning
- Knowledge management
Tech debt isn't a matter of individual issues. As mentioned earlier, it's a conscious act of sacrificing reliability today for a simpler and faster solution to release a product within a deadline. It happens and will continue to occur within software development. The main question is not "Do you have tech debt?" but "What will you do about your tech debt?" Effective tech debt management begins with developing proper software development processes like Agile and DevOps.
Mad Devs' position on technical debt
At Mad Devs, we like to view software technical debt similarly to financial debt. You repay it not just with the sum borrowed but with interest. When you need to extend the system, you must make an extra effort to implement the additional features. This extra effort is the interest you pay for the technical debt.
We believe the best way to deal with technical debt is to break up the 'sum' of the debt into smaller amounts you pay off. Spend a couple of days defeating cruft in your code, at least partly. There's a chance it might be enough for now, just like paying off a small part of your credit card debt so that you can pay off the whole amount later. Setting aside extra time to work on part of the technical debt makes future feature implementation cheaper.
Mad Devs' engineers never leave a project "as it is." Even if the previous team has accumulated heavy technical debt, we manage it by prioritizing tasks correctly. Technical debt management doesn't mean that work on new features won't continue. For us, it means that along with implementing new features, we're fixing accumulated issues.
Check out our article on tech debt management techniques to learn how Mad Devs engineers "pay off" their debt and reduce interest.